
Author Affiliations
Abstract
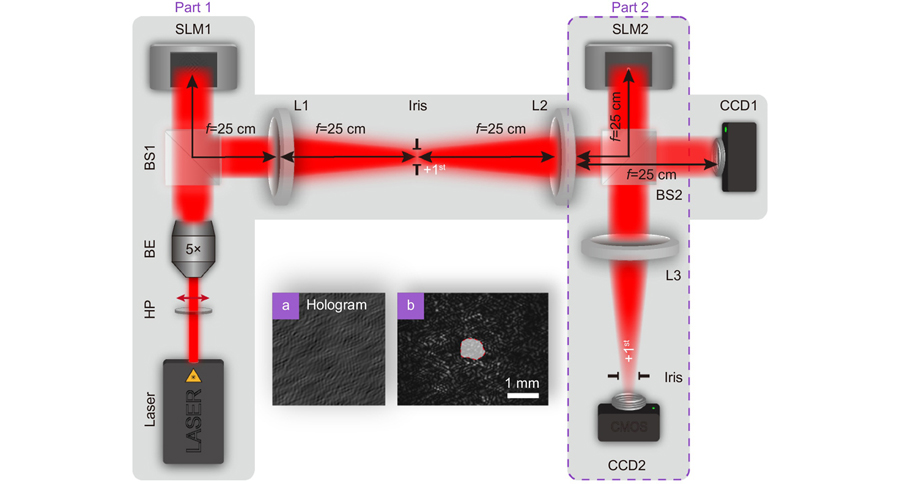
The ability to overcome the negative effects, induced by obstacles and turbulent atmosphere, is a core challenge of long-distance information transmission, and it is of great significance in free-space optical communication. The spatial-coherence structure, that characterizes partially coherent fields, provides a new degree of freedom for carrying information. However, due to the influence of the complex transmission environment, the spatial-coherence structure is severely damaged during the propagation path, which undoubtedly limits its ability to transmit information. Here, we realize the robust far-field orbital angular momentum (OAM) transmission and detection by modulating the spatial-coherence structure of a partially coherent vortex beam with the help of the cross-phase. The cross-phase enables the OAM information, quantified by the topological charge, hidden in the spatial-coherence structure can be stably transmitted to the far field and can resist the influence of obstructions and turbulence within the communication link. This is due to the self-reconstruction property of the spatial-coherence structure embedded with the cross-phase. We demonstrate experimentally that the topological charge information can be recognized well by measuring the spatial-coherence structure in the far field, exhibiting a set of distinct and separated dark rings even under amplitude and phase perturbations. Our findings open a door for robust optical signal transmission through the complex environment and may find application in optical communication through a turbulent atmosphere.
degree of coherence orbital angular momentum cross-phase topological charge information transmission Opto-Electronic Science
2024, 3(1): 240001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shandong Provincial Engineering and Technical Center of Light Manipulation & Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optics and Photonic Devices, School of Physics and Electronics, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250014, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of Light Manipulations and Applications, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250358, China
The optical coherence structures of random optical fields can determine beam propagation behavior, light–matter interactions, etc. Their performance makes a light beam robust against turbulence, scattering, and distortion. Recently, we proposed optical coherence encryption and robust far-field optical imaging techniques. All related applications place a high demand on precision in the experimental measurements of complex optical coherence structures, including their real and imaginary parts. Past studies on these measurements have mainly adopted theoretical mathematical approximations, limited to Gaussian statistic involving speckle statistic (time-consuming), or used complicated and delicate optical systems in the laboratory. In this study, we provide: a robust, convenient, and fast protocol to measure the optical coherence structures of random optical fields via generalized Arago (or Poisson) spot experiments with rigorous mathematical solutions. Our proposal only requires to capture the intensity thrice, and is applicable to any optical coherence structures, regardless of their type or optical statistics. The theoretical and experimental results demonstrated that the real and imaginary parts of the structures could be simultaneously recovered with high precision. We believe that such a protocol can be widely employed in phase measurement, optical imaging, and image transfer.
optical coherence statistical optics Arago spot optical encryption optical imaging Opto-Electronic Science
2023, 2(2): 220024

Author Affiliations
Abstract
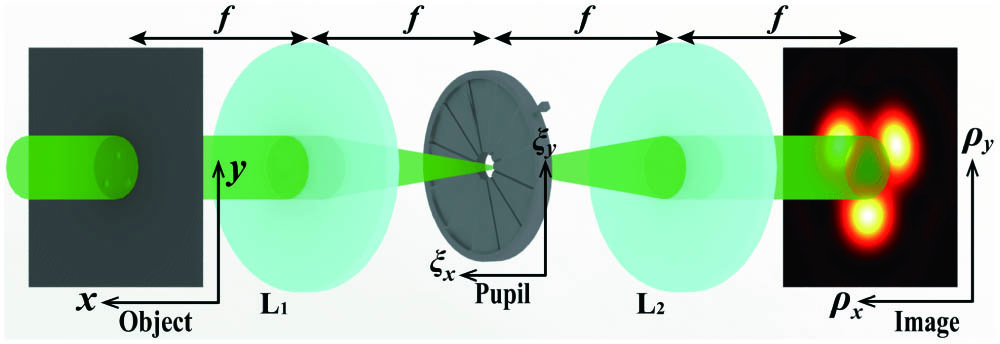
The degree of coherence (DOC) function that characterizes the second-order correlations at any two points in a light field is shown to provide a new degree of freedom for carrying information. As a rule, the DOC varies along the beam propagation path, preventing from the efficient information recovery. In this paper, we report that when a partially coherent beam carrying a cross phase propagates in free space, in a paraxial optical system or in a turbulent medium, the modulus of the far-field (focal plane) DOC acquires the same value as it has in the source plane. This unique propagation feature is employed in a novel protocol for far-field imaging via the DOC, applicable to transmission in both free-space and turbulence. The advantages of the proposed approach are the confidentiality and resistance to turbulence, as well as the weaker requirement for the beam alignment accuracy. We demonstrate the feasibility and the robustness of the far-field imaging via the DOC in the turbulent media through both the experiment and the numerical simulations. Our findings have potential applications in optical imaging and remote sensing in natural environments, in the presence of optical turbulence.
Opto-Electronic Advances
2021, 4(12): 210027-1
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shandong Provincial Engineering and Technical Center of Light Manipulations & Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optics and Photonic Device, School of Physics and Electronics, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250014, China
2 Department of Chemistry, Dalhousie University, Halifax, NS B3H 4R2, Canada
3 School of Physical Science and Technology & Collaborative Innovation Center of Suzhou Nano Science and Technology, Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, China
4 Department of Physics, University of Miami, Coral Gables, Florida 33146, USA
We suggest tailoring of the illumination’s complex degree of coherence for imaging specific two- and three-point objects with resolution far exceeding the Rayleigh limit. We first derive a formula for the image intensity via the pseudo-mode decomposition and the fast Fourier transform valid for any partially coherent illumination (Schell-like, non-uniformly correlated, twisted) and then show how it can be used for numerical image manipulations. Further, for Schell-model sources, we show the improvement of the two- and three-point resolution to 20% and 40% of the classic Rayleigh distance, respectively.
optical coherence imaging light manipulation Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(5): 052601





